
When you want to copy files between two computers that are on the same local network, often you can simply "share" a drive or folder, and copy the files the same way you would copy files from one place to another on your own PC.
What if you want to copy files from one computer to another that is halfway around the world? You would probably use your Internet connection. However, for security reasons, it is very uncommon to share folders over the Internet. File transfers over the Internet use special techniques, of which one of the oldest and most widely-used is FTP. FTP, short for "File Transfer Protocol," can transfer files between any computers that have an Internet connection, and also works between computers using totally different operating systems.
Transferring files from a client computer to a server computer is called "uploading" and transferring from a server to a client is "downloading".
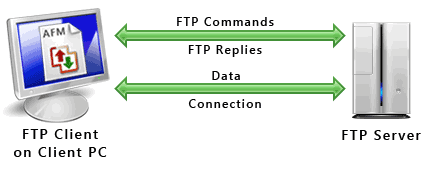
FTP uses one connection for commands and the other for sending and receiving data. FTP has a standard port number on which the FTP server "listens" for connections. A port is a "logical connection point" for communicating using the Internet Protocol (IP). The standard port number used by FTP servers is 21 and is used only for sending commands. Since port 21 is used exclusively for sending commands, this port is referred to as a command port. For example, to get a list of folders and files present on the FTP server, the FTP client issues a "LIST" command. The FTP server then sends a list of all folders and files back to the FTP Client. So what about the internet connection used to send and receive data? The port that is used for transferring data is referred to as a data port. The number of the data port will vary depending on the "mode" of the connection. (See below for Active and Passive modes.)
- FTP Navigator
- FileZilla
- CoffeeCup Free FTP
- Core FTP Lite


No comments:
Post a Comment